Exploring what is so special about extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) that deliver the extraordinary health benefits of best olive oil as well as tasting great.
Updated October 18th 2022

Summary
- The best olive oil is extra virgin olive oil (EVOO).
- Studies show that the fatty acids and antioxidants in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) can offer some powerful health benefits.
- The monounsaturated fats in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) contribute to a healthy diet.
- Saturated fats are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature and are strongly associated with raised blood cholesterol
- One tablespoon (13.5 grams) of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) typically contains
Saturated fat: 14%
Monounsaturated fat: 73% (mostly oleic acid)
Vitamin E: 13% of the Daily Value (DV)
Vitamin K: 7% of the DV - True extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is loaded with polyphenols the antioxidants some of which have powerful health benefits.
- A main polyphenol in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is oleocanthal, which has been shown to work like ibuprofen, a popular anti-inflammatory drug.
- Polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) also protects against heart disease by: reducing inflammation, a key driver of heart disease; reducing oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol; improving blood vessel health; helping to manage blood clotting; lowering blood pressure.
- The oleic acid in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is also highly resistant to oxidation and has been shown to have beneficial effects on genes linked to cancer.
- Studies have shown that a Mediterranean diet enriched with extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) improved brain function and reduced the risk of cognitive impairment.
Content
- Introduction
- What Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) And How Is It Made?
- The Fats In Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) That Contribute To A Healthy Diet
- What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)?
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) Nutrition
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) Health Benefits
- Can you cook with extra virgin olive oil (EVOO)?
- About Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil (EVOO)
Introduction
We are always delighted to come across articles that confirm our own extensive researches into the health benefits of extra virgin olive oil and it’s nutritional information. We know extra virgin olive oil is the healthiest fat in the world. Here is a wonderful summary from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/extra-virgin-olive-oil

Dietary fats are highly controversial, with debates about animal fats, seed oils, and everything in between in full force. That said, most people agree that extra virgin olive oil is incredibly healthy. Part of the Mediterranean diet, this traditional oil has been a dietary staple for some of the world’s healthiest populations.
Studies show that the fatty acids and antioxidants in olive oil can offer some powerful health benefits. This article reviews why extra virgin olive oil is the healthiest fat on earth.
What Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) And How Is It Made?
Olive oil is oil that has been pressed from olives, the fruits of the olive tree. The production process is incredibly simple — olives are pressed to extract their oil. However, lower quality versions can be extracted using chemicals, or even diluted with other, cheaper oils. Therefore, buying the right type of olive oil is crucial.
The best type is extra virgin olive oil. It’s extracted using natural methods and standardized for purity and certain sensory qualities like taste and smell. Oil that is truly extra virgin olive oil has a distinct taste and is high in polyphenol antioxidants, the main reason why it’s so beneficial.
Also, there are refined or “light” olive oils, which have often been extracted with solvents, treated with heat, or even diluted with cheaper oils like soybean or canola oil. For this reason, it’s essential to inspect the label carefully and buy from a reputable seller. Even oil that is labelled extra virgin olive oil may have been adulterated with cheaper oils.
True extra virgin olive oil is 100% natural and very high in antioxidants. Many of the lower quality olive oils have been processed and adulterated with cheaper oils.
The Fats In Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) That Contribute To A Healthy Diet
Fats are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon atom in the chain is attached to hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom determines whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated and therefore will contribute towards a healthy diet.
Saturated fats
If a fatty acid has all of the hydrogen atoms it can hold (2 per carbon atom in the chain) and all of the carbon atoms in the chain are linked by single bonds, it is described as saturated.
Saturated fats are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature and are strongly associated with raised blood cholesterol which is why nutritionists recommend eating them as little as possible. Lard, butter, hard cheeses, whole milk, animal fats and palm and coconut oils – plus products containing them – all contain high levels of saturated fat that do not support a healthy diet.
Monounsaturated Fats In Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) Support A Healthy Diet
If a pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain is linked by a double bond instead of a single bond, the fatty acid is described as monounsaturated. Fats rich in monounsaturates tend to be liquid at room temperature. Olive oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids and therefore supports a healthy diet.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of extra virgin olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Polyunsaturated fats
These contain more than one double bond and are liquid at room temperature. The main sources are vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil, corn oil and rapeseed, but not tropical oils such as coconut, palm and palm kernel oils.
Trans fats
Trans fats are created when a hydrogenation process is applied to solidify oil for use in margarines or to improve a product’s shelf life. This processing causes trans fats to act like saturated fats.
The following illustrates the differing fat contents of a range of products.
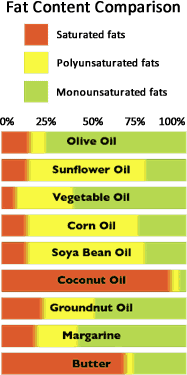
What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)?
One serving or 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil contains the following:
- 120 calories
- 10 grams of monounsaturated fat
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams of polyunsaturated fat
- 1.9 milligrams of vitamin E (10 percent of Daily Value)
- 8.1 micrograms of vitamin K (10 percent of DV)
Not All Calories Are Created Equal
As part of maintaining a healthy diet many people want to know how many calories are in olive oil. Research has shown that not all calories are necessarily equal.
In a famous study at Middlesex Hospital in London in the 1950s, two British researchers, Professor Alan Kekwick and Dr. Gaston L.S. Pawan, tested a series of diets on overweight patients. The patients on a high-carbohydrate diet consistently gained or sustained weight, even when given limited calories. Conversely, subjects on a high-fat diet lost considerably more weight than any of the other diets, even when provided with excess calories.
A more recent study published in The Journal of the American Medical Association also challenges the notion that a “calorie is just a calorie.” Led by Cara Ebbeling, PhD, associate director and David Ludwig, MD, director of the New Balance Foundation Obesity Prevention Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, the purpose of the study was to learn what kind of diet helped people maintain their new weight after successfully losing weight. The results indicated that a low-fat diet predicts weight regain, while diets featuring a moderate to high percentage of calories from fat both increased subjects’ energy expenditure and reduced the surge in their blood sugar after eating, making these diets preferable to a low-fat diet for those trying to achieve lasting weight loss.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (Evoo) Nutrition
Extra virgin olive oil is nutritious. It contains modest amounts of vitamins E and K and plenty of beneficial fatty acids.
Some more olive oil nutrition information – One tablespoon (13.5 grams) of olive oil contains the following:
- Saturated fat: 14%
- Monounsaturated fat: 73% (mostly oleic acid)
- Vitamin E: 13% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Vitamin K: 7% of the DV
Notably, extra virgin olive oil shines in its antioxidant content. Antioxidants are biologically active, and some of them can help fight serious diseases. The oil’s main antioxidants include the anti-inflammatory oleocanthal, as well as oleuropein, a substance that protects LDL (bad) cholesterol from oxidation.
Olive oil is very high in monounsaturated fats and contains a modest amount of vitamins E and K. True extra virgin olive oil is loaded with antioxidants, some of which have powerful health benefits.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) Health Benefits
Extra virgin olive oil contains anti-inflammatory substances
Chronic inflammation is believed to be among the leading drivers of many diseases, including heart disease, cancer, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and arthritis. Some speculate that olive oil’s ability to fight inflammation is behind its many health benefits.
Oleic acid, the most prominent fatty acid in olive oil, has been found to reduce inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein. However, the oil’s main anti-inflammatory effects seem to be due to its antioxidants, primarily oleocanthal, which has been shown to work like ibuprofen, a popular anti-inflammatory drug. Researchers estimate that the amount of oleocanthal in 50 ml (about 3.4 tablespoons) of extra virgin olive oil exerts effects similar to those of 10% of the adult ibuprofen dosage for pain relief. Also, one study showed that substances in olive oil can reduce the expression of genes and proteins that mediate inflammation.
Keep in mind that chronic, low-level inflammation is usually fairly mild, and it takes years or decades for it to do damage. Using extra virgin olive oil may help prevent this from happening, leading to a reduced risk of various inflammatory diseases, especially heart disease. Olive oil contains oleic acid and oleocanthal, two nutrients that can fight inflammation. This may be the main reason for olive oil’s health benefits.
Extra virgin olive oil (Evoo) and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke, are among the most common causes of death in the world. Many observational studies show that death from these diseases is low in certain areas of the world, especially in countries around the Mediterranean Sea. This observation originally spurred interest in the Mediterranean diet, which is supposed to mimic the way the people in those countries eat. Studies on the Mediterranean diet show that it can help prevent heart disease. In one major study, it reduced heart attacks, strokes, and death by 30%.
Extra virgin olive oil protects against heart disease via numerous mechanisms:
- Reducing inflammation: Olive oil protects against inflammation, a key driver of heart disease
- Reduces oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol: The oil protects LDL particles from oxidative damage, a key factor in the development of heart disease
- Improves blood vessel health: Olive oil improves the function of the endothelium, which is the lining of the blood vessels
- Helps manage blood clotting: Some studies suggest that olive oil can help prevent unwanted blood clotting, a key feature of heart attacks and strokes
- Lowers blood pressure: One study in patients with elevated blood pressure found that olive oil reduced blood pressure significantly and lowered the need for blood pressure medication by 48%
Given the biological effects of extra virgin olive oil, it’s not surprising that people who consume the greatest amounts of it are significantly less likely to die from heart attacks and strokes.
Dozens — if not hundreds — of animal and human studies have shown that olive oil has major benefits for the heart. In fact, the evidence is strong enough to recommend that people who have or are at a high risk of developing heart disease include plenty of extra virgin olive oil in their diets.
Olive oil may be one of the healthiest foods you can eat for heart health. It reduces blood pressure and inflammation, protects LDL particles from oxidation, and may help prevent unwanted blood clotting.
Other health benefits of extra virgin olive oil (Evoo)
Although olive oil has mostly been studied for its effects on heart health, its consumption has also been associated with a number of other health benefits.
Olive oil and cancer
Cancer is a common cause of death and characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells.
Studies have shown that people living in the Mediterranean countries have a fairly low risk of cancer, and some have speculated that olive oil has something to do with it. One potential contributor to cancer is oxidative damage due to harmful molecules called free radicals. However, extra virgin olive oil is high in antioxidants that reduce oxidative damage., 29Trusted Source).
The oleic acid in extra virgin olive oil is also highly resistant to oxidation and has been shown to have beneficial effects on genes linked to cancer (30Trusted Source, 31Trusted Source).
Many test-tube studies have observed that compounds in olive oil can help fight cancer at the molecular level (32, 33, 34Trusted Source). That said, controlled trials in humans have yet to study whether olive oil helps prevent cancer.
Extra Virgin Olive oil (Evoo) and Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the world’s most common neurodegenerative disease and a leading cause of dementia.
One feature of Alzheimer’s is a buildup of protein tangles called beta-amyloid plaques in certain neurons in the brain.
A study in mice observed that a substance in olive oil can help clear these plaques (35).
Additionally, a controlled study in humans showed that a Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil improved brain function and reduced the risk of cognitive impairment (36Trusted Source). Preliminary evidence suggests that olive oil can help fight cancer and Alzheimer’s disease, although human studies need to confirm this.
Can you cook with extra virgin olive oil (Evoo)?
During cooking, fatty acids can oxidize, meaning they react with oxygen and become damaged. The double bonds in fatty acid molecules are mostly responsible for this. For this reason, saturated fats (no double bonds) are resistant to high heat, while polyunsaturated fats (many double bonds) are sensitive and become damaged.
The nutritional info of olive oil, which contains mostly monounsaturated fatty acids (only one double bond), is fairly resistant to high heat. In one study, researchers heated extra virgin olive oil to 356°F (180°C) for 36 hours. The oil was highly resistant to damage (37Trusted Source). Another study used olive oil for deep-frying, and it took 24–27 hours for it to reach damage levels that were deemed harmful (38Trusted Source). Overall, olive oil seems to be very safe even for cooking at a fairly high heat. In essence good for the bodies nutritional needs.
The bottom line
Olive oil is super healthy and very nutritious. For those who have heart disease or are at a high risk of developing it, olive oil is most definitely a superfood. However, be sure to purchase extra virgin olive oil that hasn’t been diluted with cheaper oils. The benefits of this wonderful fat are among the few things that most people in nutrition agree upon.
About Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil
For health conscious, discerning food lovers across all cultures and culinary backgrounds, Morocco Gold is a natural, unfiltered, ultra premium, polyphenol rich extra virgin olive oil, whose exquisite taste and health enhancing qualities are guaranteed by our rigorous testing, provenance and authenticity, and strict adherence to single estate sourcing, with no blending or mixing.

What is extra virgin olive oil good for : how is using Morocco Gold going to boost my nutrition?
Incredibly versatile, Morocco Gold is one of the best and most nutritious extra virgin olive oils for cooking and salad dressing. Here is some nutritional info: It is high in polyphenols and cold pressed within 24 hours of harvesting.
Morocco Gold shows why extra virgin olive oil is the healthiest fat on earth. It can also be used as an extra virgin olive oil for hair and as an extra virgin olive oil for skin.
Our gold award winning extra virgin olive oil represents the very best extra virgin olive oil.
The oil is produced from olives grown in the foothills of the Atlas Mountains, where the unique micro-climate and geology provides ideal conditions for olive growing. Morocco Gold combines centuries of local cultivation and harvesting knowledge, with our rigorous traceability and quality assurance procedures to bring what is locally considered a ‘noble food’ to international markets.
The olive oil is produced from the Picholine Marocaine olive. Our olives are hand-picked early in the harvesting season when the fruit is young and first cold pressed within 24 hours of picking. Some more olive oil nutritional info: There is no mixing or blending with other oils to ensure genuine extra virgin quality.
As a result this gives Morocco Gold it’s distinctive green fruitiness, hints of sweet almonds, fresh turf and a hint of herbs. It has the distinctive ‘pepperiness’ (not too aggressive) of a fine extra virgin olive oil which as a consequence gives Morocco Gold a clean, well balanced finish.
