The Heath Benefits Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Enhanced Excercise Performance
Updated 18th March 2024

Summary:
- New report lists extra virgin olive is one of most energy-dense foods around with around nine calories per gram of fat.
- When it comes to extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), there are many benefits that can be gained from its regular consumption. Not only is EVOO the highest quality and best olive oil, but it is also rich in polyphenols—micronutrients known to positively affect heart health, digestion and even skin. Polyphenols also act as antioxidants and may protect against certain types of cancer.
- But who knew extra virgin olive oil could also boost exercise performance? A recent study suggests that athletes who consume extra virgin olive oil before their workout experienced more efficient oxygen distribution in muscles, leading to enhanced performance and better endurance over time.
- So next time you hit the gym, make sure you have your extra virgin olive oil intake sorted; it just may lead to increased longevity!
Contents:
- Runners World lists extra virgin olive oil as key energy-dense food to power your run.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Combat Age Related Diseases
- Energy Boost From Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Enhanced Fitness
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil For Muscle Recovery
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil For Exercise At All Ages
- Fat Content Comparison. Increase Your Health Benefits By Using Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Runners World lists extra virgin olive oil as key energy-dense food to power your run.
New research has highlighted extra virgin olive oil as one of the most energy-dense foods, making it an excellent addition to any runner’s diet. Known for its rich flavour and numerous health benefits, this versatile oil provides a concentrated source of energy that can help fuel long runs and intense training sessions.
For runners looking to optimize their performance and endurance, incorporating extra virgin olive oil into meals could be a game-changer. Whether drizzled over salads, mixed into smoothies, or used in cooking, this powerhouse ingredient supports sustained energy levels and overall well-being.
The article states:
Liquid fats, like extra virgin olive oil, are the most energy-dense foods around, with each gram of fat supplying nine calories. But, this staple of the much-researched Mediterranean diet is proof that some fatty items do the body good.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that adding half a tablespoon or more of extra virgin olive oil to your diet could lower your risk of death from heart disease and cancer by 19% and 17% respectively. Extra virgin olive oil was also associated with a 29% lower mortality risk from neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. What’s more, replacing about 10g a day (about 3/4 tbsp) of butter, margarine, mayonnaise or dairy fat with the equivalent amount of olive oil was associated with a lower risk of early death by up to 34%.
According to the findings of a separate report, eating a moderate amount of extra virgin olive oil can reduce inflammation, your blood pressure and your risk of developing certain cancers.
‘Polyphenols in olive oil have been associated with reducing morbidity, which is related to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, these properties can also help to enhance healing from sport and minimise the damaging effects of free radicals released during intense training.’
Emily Edison, owner of Momentum Nutrition.
Edison also points out that the monounsaturated fats in extra virgin olive oil can contribute to a reduction in LDL (‘bad’) cholesterol when it is used to replace other fats in the diet.
The fat pressed from olives is also source of vitamin E, too, which acts as an antioxidant to protect our cells from the harmful effects of circulating free radicals. This is another way that extra virgin olive oil may help athletes to recover more effectively from their training.
While extra virgin olive oil is not the only type of olive oil you can get your hands on, Edison says that it is the highest quality and healthiest grade. ‘It is not treated with heat or chemicals, thus maintaining the phenol and nutrient content.’
Emily Edison, owner of Momentum Nutrition.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Combat Age Related Diseases
The healthy fat in extra virgin olive oil appears to activate pathways in cells linked to longer life span, according to a new study.
A recent report, published in Sciencedaily.com suggests that olive oil in the diet may extend life and mitigate aging-related diseases.
According to new research by the University of Minnesota Medical School, olive oil, a staple ingredient of the Mediterranean diet, appears to have properties that promote longevity and decrease the risk of age-related disease like diabetes and heart disease.
Doug Mashek, the lead researcher, said that looking at the way olive oil affected human cells in petri dishes indicated that the fats in olive oil activated cell pathways in the body that are linked to longer life.
“We found that the way this fat works is it first has to get stored in microscopic things called lipid droplets, which is how our cells store fat,” Mashek said. “And then, when the fat is broken down during exercising or fasting, for example, is when the signalling and beneficial effects are realized.”
Energy Boost From Extra Virgin Olive Oil
At its most basic, olive oil provides energy, something athletes never want to be without. Compared to the sedentary who should consume no more than 15% of their calories from fat, athletes need anywhere from 20%-30%. This is true for both endurance and high-intensity sports. Fat is the body’s main fuel during low-intensity lengthy endeavours like triathlons and marathons. But it’s just as necessary for high-intensity sports too. Carbohydrates may be the central fuel for high-intensity activities but without fat, carbohydrate energy cannot be released.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Enhanced Fitness
At Morocco Gold, we find that lovers of quality extra virgin olive oil are often passionate about keeping in physical and mental shape. As as well as their love of great food they are interested in the benefits of extra virgin olive oil and fitness.

They love to try out new clean eating or healthy recipes and to experiment with food. They do also love to know exactly what it is in their food that makes it special.
There are many articles that discuss the well-known health benefits of extra virgin olive oil including:
- Reducing risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Having a beneficial effect on ulcers and gastritis
- Maintaining the digestive tract in good health.
- Helping to reduce blood pressure
- Helping control healthy cholesterol levels
- Easing or preventing diabetes
- Lessening the severity of osteoporosis
Extra Virgin Olive Oil For Muscle Recovery
Muscles have a hard time during athletic training and need immediate recovery, which includes repair, strengthening and muscle building. EVOO is better than other fat sources in helping cells absorb cholesterol and convert it to testosterone. This is critical to the body’s muscle building process. Moreover, its combination of oleic acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids work together to build bone tissue and allow the body to regenerate.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil For Exercise At All Ages
Whilst many of these health benefits of extra virgin olive oil combat conditions that come as part of the natural ageing process, there are also clear benefits for people of all ages who are passionate about exercise and keeping fit as part of their lifestyle choices.
According to sports dietitians Kelly Jones, M.S., R.D. and Lori Nedescu, M.S., R.D.N. olive oil is one of the healthiest oils because of its heart-healthy fats.
Fat is a nutrient with important functions. It is a rich source of energy, providing more than double that of either carbohydrate or protein. It is a carrier for the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. It provides the essential fatty acids, linoleic and alpha-linolenic acid, which are polyunsaturated.
Fat Content Comparison. Increase Your Health Benefits By Using Extra Virgin Olive Oil
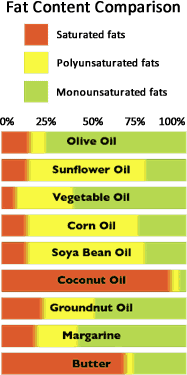
Not all Fats are the Same
Fats are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon atom in the chain is attached to hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom determines whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated.
Saturated fats
If a fatty acid has all of the hydrogen atoms it can hold (2 per carbon atom in the chain) and all of the carbon atoms in the chain are linked by single bonds, it is described as saturated.
Saturated fats are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature and are strongly associated with raised blood cholesterol which is why nutritionists recommend eating them as little as possible. Lard, butter, hard cheeses, whole milk, animal fats and palm and coconut oils – plus products containing them – all contain high levels of saturated fat.
Monounsaturated fats
If a pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain is linked by a double bond instead of a single bond, the fatty acid is described as monounsaturated. Fats rich in monounsaturates tend to be liquid at room temperature. Olive Oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Polyunsaturated fats
These contain more than one double bond and are liquid at room temperature. The main sources are vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil, corn oil and rapeseed, but not tropical oils such as coconut, palm and palm kernel oils.
Trans fats
Trans fats are created when a hydrogenation process is applied to solidify oil for use in margarines or to improve a product’s shelf life. This processing causes trans fats to act like saturated fats.
What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
One serving or 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil contains the following:
- 120 calories
- 10 grams of monounsaturated fat
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams of polyunsaturated fat
- 1.9 milligrams of vitamin E (10 percent of Daily Value)
- 8.1 micrograms of vitamin K (10 percent of DV)
Athletes like cyclists, long distance runners, tennis players and other high-performance sports and exercise enthusiasts also stress their heart out more than the average person, according to Jones, so it’s beneficial to add nutrients to your diet that protect it. Monounsaturated fats are also anti-inflammatory, which helps with muscle recovery. Working out can cause micro-tears in your muscles, which can lead to inflammation, muscle pain, and soreness, but anti-inflammatories can help calm that reaction.
Plus, vitamin E is an antioxidant that the majority of Americans (and the rest of us) don’t get enough of, Jones says. This nutrient helps boost your immune system and protect your body against heart disease and certain types of cancer. In addition, antioxidants protect your cells against damage, especially those in your muscles and lungs, which are extremely important when it comes to your performance on the bike.
Vitamin K is important for absorbing fats like the monounsaturated ones in olive oil. If you don’t get enough of this vitamin, your body will have trouble using it effectively.
“When you’re doing endurance exercise, you need healthy fats to fuel your body,” Dr Jones says. “One quarter of your calories should come from fat, and I recommend including [fats] in every meal and snack in small amounts.” This will help you feel satiated as the day goes on.
“Extra-virgin olive oil is the closest to nature and the least refined,” Jones says. “The more refined your olive oil is, that’s where you’re not sure how it’s been processed. It could be treated with chemicals or treated with high heat, which may damage its antioxidants.”
So, imagine your body is a high-performance engine. Keeping it topped up with natures highest performing ‘engine oil’ will ensure smooth performance for decades to come.
